Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT or Claude are highly effective at generating fluent, human-like text. However, when used on their own, they are limited by the data they were trained on and cannot directly access up-to-date or domain-specific information.
This limitation often leads to generic answers or, in some cases, confident but incorrect responses. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) addresses this challenge by combining information retrieval with generative AI.
Instead of relying solely on what the model remembers from training, RAG enables LLMs to retrieve relevant external knowledge before generating a response, making outputs more accurate, contextual, and reliable.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
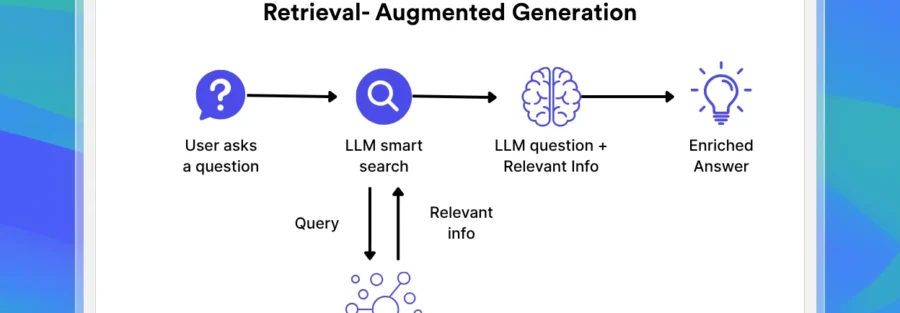
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is an AI architecture that enhances language model outputs by integrating an external knowledge retrieval step into the generation process.
In a RAG system, the model first searches for relevant information from a knowledge base, document repository, or database. The retrieved content is then injected into the prompt used by the LLM to generate the final answer.
This approach allows language models to produce responses grounded in verified, up-to-date, and domain-specific data rather than relying solely on statistical patterns learned during training.
Why RAG Improves LLM Responses
Traditional LLMs operate on static knowledge. Once training is complete, the model has no awareness of new documents, updated policies, or proprietary enterprise data.
RAG overcomes this limitation by dynamically connecting the model to external sources of truth. As a result, responses are more accurate, less prone to hallucination, and better aligned with real-world context.
This is especially valuable for organizations working with fast-changing information or internal knowledge that cannot be embedded directly into the model.
How Retrieval-Augmented Generation Works
Although implementations vary, most RAG systems follow a similar workflow.
1. Knowledge Indexing
Documents such as PDFs, web pages, or internal reports are processed and converted into numerical representations known as embeddings. These embeddings are stored in a vector database optimized for similarity search.
2. Query Retrieval
When a user submits a question, the query is converted into an embedding and compared against the indexed data to identify the most relevant information.
3. Prompt Augmentation
The retrieved content is combined with the user’s original query, creating a richer prompt that provides context and factual grounding.
4. Response Generation
The language model uses this augmented prompt to generate a response that incorporates both its linguistic capabilities and the retrieved external knowledge.
Key Benefits of RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation offers several advantages over standalone language models.
Improved Accuracy:
By grounding responses in retrieved documents, RAG significantly reduces hallucinations
and factual errors.
Domain-Specific Intelligence:
RAG enables LLMs to work effectively with specialized or proprietary knowledge without
retraining the model.
Lower Operational Cost:
Updating knowledge sources is far more efficient than retraining or fine-tuning large
language models.
Traceability and Trust:
Retrieved sources can be referenced or cited, increasing transparency and user trust.
Where RAG Is Most Effective
RAG is particularly well-suited for use cases where accuracy and context are critical.
• Enterprise knowledge assistants and internal search tools
• Customer support systems based on product documentation
• Research and analysis platforms requiring source grounding
• Legal, regulatory, and compliance applications
Conclusion
Retrieval-Augmented Generation transforms large language models from static text generators into dynamic, knowledge-aware systems.
By combining retrieval mechanisms with generative capabilities, RAG enables organizations to deploy AI solutions that are more accurate, reliable, and aligned with real business needs.
As enterprises increasingly adopt AI at scale, RAG is becoming a foundational pattern for building trustworthy and production-ready LLM applications.







2 Comments
Riva Collins
It’s no secret that the digital industry is booming. From exciting startups to need ghor
global and brands, companies are reaching out.
Obila Doe
It’s no secret that the digital industry is booming. From exciting startups to need ghor hmiu
global and brands, companies are reaching out.