Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer an experimental technology reserved for research labs.
Today, it has become a strategic capability for organizations seeking efficiency, scalability,
and competitive advantage.
However, AI is often misunderstood. Terms such as Machine Learning, Deep Learning,
and Generative AI are frequently used interchangeably, leading to confusion,
poor technology choices, and unrealistic expectations.
This article explains the core AI technologies in a clear and practical way,
focusing on how they work, where they are used, and how organizations should approach them.
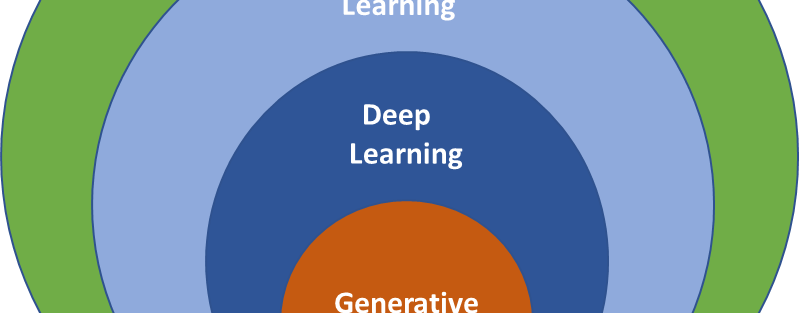
AI Is a Technology Stack, Not a Single Tool
Artificial Intelligence is not a single technology.
It is a stack of techniques and models, each designed to solve specific types of problems.
Understanding this stack is essential to selecting the right AI approach
and avoiding unnecessary complexity.
Core AI Technologies Explained
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is the foundation of most AI systems in use today.
It enables systems to learn patterns from data without being explicitly programmed
for every possible scenario.
Key ML Approaches
Supervised Learning
Uses labeled data to predict outcomes or classify information.
Typical use cases include demand forecasting, churn prediction, and fraud detection.
Unsupervised Learning
Identifies hidden patterns in unlabeled data.
Common applications include clustering, segmentation, and anomaly detection.
Reinforcement Learning
Learns through trial and error by interacting with an environment.
It is often used for optimization problems, control systems, and automation.
Business Applications
• Demand forecasting and planning
• Fraud detection and risk scoring
• Customer segmentation and personalization
• Predictive maintenance
• Operational optimization
2. Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that uses multi-layer neural networks
to process complex and large-scale data.
It excels at handling unstructured data such as images, audio, video, and free text,
where traditional ML techniques reach their limits.
Deep Learning typically requires large datasets and high computational resources,
but delivers superior accuracy in tasks such as image recognition,
speech recognition, and natural language understanding.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing enables machines to understand, interpret,
and generate human language.
Modern NLP systems can analyze sentiment, extract meaning from documents,
summarize content, and interact with users in natural language.
NLP is widely used in chatbots, document automation,
customer support platforms, and enterprise knowledge systems.
4. Generative AI
Generative AI represents a major evolution in AI capabilities.
Instead of only analyzing or predicting outcomes,
these systems can generate new content.
This includes text, code, images, audio, and video,
powered by large language models and foundation models.
Generative AI enables use cases such as enterprise copilots,
content generation, code assistance, and knowledge augmentation.
However, it also introduces new risks related to accuracy,
security, and governance that must be managed carefully.
How the AI Technology Stack Fits Together
A production-grade AI system typically includes:
• A data layer for structured and unstructured data
• A model layer using ML, Deep Learning, or Generative AI
• Training and validation pipelines
• Deployment through applications or APIs
• Monitoring, governance, and performance management
Successful AI initiatives focus on integration and lifecycle management,
not isolated models.
Common AI Technology Misconceptions
Many AI initiatives fail due to misconceptions such as:
• AI replaces humans entirely
• More complex models always deliver better results
• Generative AI removes the need for data strategy
• AI success is purely a technology challenge
In reality, AI success depends on business alignment,
data quality, governance, and skills.
How Organizations Should Approach AI Technologies
Rather than asking which AI model to use,
organizations should start with business questions:
• What problem are we trying to solve?
• Do we need prediction, automation, or content generation?
• What data is available today?
• What level of explainability and control is required?
Technology should follow strategy — not the opposite.
Conclusion
AI technologies are powerful when applied with clarity and structure.
Understanding the differences between Machine Learning,
Deep Learning, NLP, and Generative AI
is essential to making the right investments
and scaling AI successfully.
At VisionStratAI, we focus on applied AI,
helping organizations turn AI technologies
into measurable business value.







2 Comments
Riva Collins
It’s no secret that the digital industry is booming. From exciting startups to need ghor
global and brands, companies are reaching out.
Obila Doe
It’s no secret that the digital industry is booming. From exciting startups to need ghor hmiu
global and brands, companies are reaching out.